Assembly Line Balancing (SALBP)¶
Principles learned¶
- Set succession constraints
- Use intermediate variables
- Use set variables with operator “find”
Problem¶
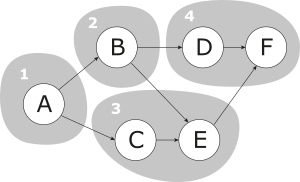
We consider a simple assembly line balancing problem (SALBP) as defined by Prof. Dr. Armin Scholl, Friedrich Schiller University Jena. We have a set of tasks that must be gathered in groups called stations. Each task requires a certain processing time. Moreover, some tasks cannot be performed if some other tasks have not been completed before. Finally, the sum of the tasks’ processing times in each station cannot exceed a given limit. Therefore, the goal is to minimize the number of stations such that the cycle time limit constraints and the tasks’ order are satisfied. On the left diagram, the tasks are the letter circles, the order constraints are represented by arrows and the grey areas are the stations.
Download the exampleData¶
The instances provided come from Alena Otto. They are formatted into the following format:
- Number of tasks
- Cycle time limit
- Tasks’ processing times
- Precedence relations
Program¶
This LocalSolver model defines a sequence of set variables called “station”. Each set represents a station which can either contain some tasks or be empty. To ensure that each task belongs to an unique station, set variables must form a partition.
We state an upper bound for the number of stations equals to the number of tasks according to the naive solution where each task is contained in a different station.
The number of used stations is computed as the number of non-empty sets and should be minimized. The cycle time constraint is written with a variadic sum of processing times over the tasks of each set. The succession constraints verify that for each task, its station’s number is inferior or equal to its successors’ ones thanks to the “find” operator.
- Execution:
- localsolver assembly_line_balancing.lsp inFileName=instances/instance_n20_1.alb [lsTimeLimit=] [solFileName=]
/********** assembly_line_balancing.lsp **********/
use io;
/* Read instance data. */
function input() {
local usage = "Usage: localsolver assembly_line_balancing.lsp "
+ "inFileName=inputFile [lsTimeLimit=timeLimit] [solFileName=solFile]\n";
if(inFileName == nil) throw usage;
local inFile = io.openRead(inFileName);
inFile.readln();
// Read number of tasks
nbTasks = inFile.readInt();
maxNbStations = nbTasks;
inFile.readln();
// Read the cycle time limit
cycleTime = inFile.readInt();
for [i in 0..4] inFile.readln();
// Read the processing times
for [t in 0..nbTasks-1]
processingTime[inFile.readInt()-1] = inFile.readInt();
// Read the successors' relations
for [t in 0..nbTasks-1]
successors[t] = {};
inFile.readln();
local line = inFile.readln().split(",");
while(line.count() > 1) {
local predecessor = toInt(line[0]) - 1;
local successor = toInt(line[1]) - 1;
successors[predecessor].add(successor);
line = inFile.readln().split(",");
}
inFile.close();
}
/* Declare the optimization model. */
function model() {
// Decision variables: station[s] is the set of tasks assigned to station s
station[s in 0..maxNbStations-1] <- set(nbTasks);
constraint partition[s in 0..maxNbStations-1](station[s]);
// Objective: nbUsedStations is the total number of used stations
nbUsedStations <- sum[s in 0..maxNbStations-1](count(station[s]) > 0);
// All stations must respect the cycleTime constraint
timeInStation[s in 0..maxNbStations-1] <- sum(station[s], i => processingTime[i]);
for [s in 0..maxNbStations-1]
constraint timeInStation[s] <= cycleTime;
// The stations must respect the succession's order of the tasks
taskStation[i in 0..nbTasks-1] <- find(station, i);
for[i in 0..nbTasks-1][j in successors[i]]
constraint taskStation[i] <= taskStation[j];
// Minimization of the number of active stations
minimize nbUsedStations;
}
/* Parametrize the solver. */
function param() {
if (lsTimeLimit == nil) lsTimeLimit = 20;
}
/* Write the solution in a file following the following format:
* - value of the objective (number of stations)
* - number of tasks
* - task's number, station's number */
function output() {
if(solFileName == nil) return;
local solFile = io.openWrite(solFileName);
solFile.println(nbUsedStations.value);
solFile.println(nbTasks);
for[i in 0..nbTasks-1]
solFile.println(i + 1, ",", taskStation[i].value + 1);
}
- Execution (Windows)
- set PYTHONPATH=%LS_HOME%\bin\pythonpython assembly_line_balancing.py instances\instance_n20_1.alb
- Execution (Linux)
- export PYTHONPATH=/opt/localsolver_10_5/bin/pythonpython assembly_line_balancing.py instances/instance_n20_1.alb
########## assembly_line_balancing.py ##########
import localsolver
import sys
#
# Functions to read the instances
#
def read_elem(filename):
with open(filename) as f:
return [str(elem) for elem in f.read().split()]
def read_instance(instance_file):
file_it = iter(read_elem(instance_file))
for i in range(3):
to_throw = next(file_it)
# Read number of tasks
nbTasks = int(next(file_it))
maxNbStations = nbTasks
for i in range(2):
to_throw = next(file_it)
# Read the cycle time limit
cycleTime = int(next(file_it))
for i in range(5):
to_throw = next(file_it)
# Read the processing times
processingTimeDict = {}
for i in range(nbTasks):
task = int(next(file_it)) - 1
processingTimeDict[task] = int(next(file_it))
for i in range(2):
to_throw = next(file_it)
processingTime = [elem[1] for elem in sorted(processingTimeDict.items(), key=lambda x: x[0])]
# Read the successors' relations
successors = {}
while True:
try:
pred, succ = next(file_it).split(',')
pred = int(pred) -1
succ = int(succ) -1
if pred in successors:
successors[pred].append(succ)
else:
successors[pred] = [succ]
except:
break
return nbTasks, maxNbStations, cycleTime, processingTime, successors
#
# Modeling and solve
#
def main(instance_file, output_file, time_limit):
nbTasks, maxNbStations, cycleTime, processingTime, successors = read_instance(instance_file)
with localsolver.LocalSolver() as ls:
# Declare the optimization model
model = ls.model
# Decision variables: station[s] is the set of tasks assigned to station s
station = [model.set(nbTasks) for s in range(maxNbStations)]
station_array = model.array(station)
model.constraint(model.partition(station_array))
# Objective: nbUsedStations is the total number of used stations
nbUsedStations = model.sum((model.count(station[s]) > 0) for s in range(maxNbStations))
# All stations must respect the cycleTime constraint
processingTime_array = model.array(processingTime)
time_selector = model.lambda_function(lambda i : processingTime_array[i])
timeInStation = [model.sum(station[s], time_selector) for s in range(maxNbStations)]
for s in range(maxNbStations):
model.constraint(timeInStation[s] <= cycleTime)
# The stations must respect the succession's order of the tasks
taskStation = [model.find(station_array, i) for i in range(nbTasks)]
for i in range(nbTasks):
if i in successors.keys():
for j in successors[i]:
model.constraint(taskStation[i] <= taskStation[j])
# Minimization of the number of active stations
model.minimize(nbUsedStations)
model.close()
#
# Parameterize the solver
#
ls.param.time_limit = time_limit
ls.solve()
# Write the solution in a file following the format:
# - 1st line: value of the objective
# - 2nd line: number of tasks
# - following lines: task's number, station's number
if output_file is not None:
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.write("%d\n" % nbUsedStations.value)
f.write("%d\n" % nbTasks)
for i in range(nbTasks):
f.write("{},{}\n".format(i+1, taskStation[i].value+1))
if __name__ == '__main__':
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python assembly_line_balancing.py instance_file [output_file] [time_limit]")
sys.exit(1)
instance_file = sys.argv[1]
output_file = sys.argv[2] if len(sys.argv) >= 3 else None
time_limit = int(sys.argv[3]) if len(sys.argv) >= 4 else 20
main(instance_file, output_file, time_limit)
- Compilation / Execution (Windows)
- cl /EHsc assembly_line_balancing.cpp -I%LS_HOME%\include /link %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolver105.libassembly_line_balancing instances\instance_n20_1.alb
- Compilation / Execution (Linux)
- g++ assembly_line_balancing.cpp -I/opt/localsolver_10_5/include -llocalsolver105 -lpthread -o assembly_line_balancing./assembly_line_balancing instances/instance_n20_1.alb
/********** assembly_line_balancing.cpp **********/
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include "localsolver.h"
using namespace localsolver;
using namespace std;
class ALBInstance {
public:
int nbTasks;
int nbMaxStations;
int cycleTime;
string to_throw;
vector<int> processingTime;
vector<vector<int>> successors;
/* Read instance data */
void readInstance(const string& fileName) {
ifstream infile;
infile.exceptions(ifstream::failbit | ifstream::badbit);
infile.open(fileName.c_str());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
infile >> to_throw;
// Read number of tasks
infile >> nbTasks;
nbMaxStations = nbTasks;
processingTime.resize(nbTasks);
successors.resize(nbTasks);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
infile >> to_throw;
// Read the cycle time limit
infile >> cycleTime;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
infile >> to_throw;
// Read the processing times
for (int i = 0; i < nbTasks; ++i) {
int task;
infile >> task;
infile >> processingTime[task - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
infile >> to_throw;
// Read the successors' relations
string delimiter = ",";
while (infile.eof() != true) {
string relation;
infile >> relation;
string predecessor = relation.substr(0, relation.find(delimiter));
if(predecessor == relation)
break;
string successor = relation.substr(relation.find(delimiter)+1, relation.size());
successors[stoi(predecessor)-1].push_back(stoi(successor)-1);
}
infile.close();
}
ALBInstance(const string& fileName) {
readInstance(fileName);
}
};
class AssemblyLineBalancing {
private:
// LocalSolver
LocalSolver localsolver;
// Instance data
const ALBInstance* instance;
// Decision variables
vector<LSExpression> station;
// Intermediate expressions
vector<LSExpression> timeInStation;
vector<LSExpression> taskStation;
// Objective
LSExpression nbUsedStations;
public:
// Constructor
AssemblyLineBalancing(const ALBInstance* albi) : instance(albi) {
}
void solve(int limit) {
// Declare the optimization model
LSModel model = localsolver.getModel();
// station[s] is the set of tasks assigned to station s
station.resize(instance->nbMaxStations);
LSExpression stationArray = model.array();
for(int s = 0; s < instance->nbMaxStations; ++s) {
station[s] = model.setVar(instance->nbTasks);
stationArray.addOperand(station[s]);
}
model.constraint(model.partition(stationArray));
// nbUsedStations is the total number of used stations
nbUsedStations = model.sum();
for (int s = 0; s < instance->nbMaxStations; ++s)
nbUsedStations.addOperand((model.count(station[s]) > 0));
// All stations must respect the cycleTime constraint
timeInStation.resize(instance->nbMaxStations);
LSExpression processingTimeArray = model.array(instance->processingTime.begin(), instance->processingTime.end());
LSExpression timeSelector = model.lambdaFunction([&](LSExpression i) { return processingTimeArray[i]; });
for (int s = 0; s < instance->nbMaxStations; ++s) {
timeInStation[s] = model.sum(station[s], timeSelector);
model.constraint(timeInStation[s] <= instance->cycleTime);
}
// The stations must respect the succession's order of the tasks
taskStation.resize(instance->nbTasks);
for (int i = 0; i < instance->nbTasks; ++i) {
taskStation[i] = model.find(stationArray, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < instance->nbTasks; ++i)
for (int j : instance->successors[i])
model.constraint(taskStation[i] <= taskStation[j]);
// Minimization of the number of active stations
model.minimize(nbUsedStations);
model.close();
// Parametrize the solver
localsolver.getParam().setTimeLimit(limit);
localsolver.solve();
}
/* Write the solution in a file following the format:
* - 1st line: value of the objective
* - 2nd line: number of tasks
* - following lines: task's number, station's number */
void writeSolution(const string& fileName) {
ofstream outfile;
outfile.exceptions(ofstream::failbit | ofstream::badbit);
outfile.open(fileName.c_str());
outfile << nbUsedStations.getIntValue() << endl;
outfile << instance->nbTasks << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < instance->nbTasks; ++i)
outfile << i + 1 << "," << taskStation[i].getIntValue() + 1 << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc < 2) {
cerr << "Usage: assembly_line_balancing inputFile [outputFile] [timeLimit]" << endl;
return 1;
}
const char* instanceFile = argv[1];
const char* solFile = argc > 2 ? argv[2] : NULL;
const char* strTimeLimit = argc > 3 ? argv[3] : "20";
ALBInstance instance(instanceFile);
AssemblyLineBalancing model(&instance);
try {
model.solve(atoi(strTimeLimit));
if (solFile != NULL) model.writeSolution(solFile);
return 0;
} catch (const exception& e) {
cerr << "An error occurred: " << e.what() << endl;
return 1;
}
}
- Compilation / Execution (Windows)
- copy %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolvernet.dll .csc AssemblyLineBalancing.cs /reference:localsolvernet.dllAssemblyLineBalancing instances\instance_n20_1.alb
/********** AssemblyLineBalancing.cs **********/
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using localsolver;
public class ALBInstance
{
public int nbTasks;
public int nbMaxStations;
public int cycleTime;
public int[] processingTime;
public List<int>[] successors;
// Constructor
public ALBInstance(string fileName)
{
ReadInstance(fileName);
}
/* Read instance data */
void ReadInstance(string fileName)
{
using (StreamReader input = new StreamReader(fileName))
{
string[] line;
input.ReadLine();
// Read number of tasks
nbTasks = int.Parse(input.ReadLine());
nbMaxStations = nbTasks;
processingTime = new int[nbTasks];
successors = new List<int>[nbTasks];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
input.ReadLine();
// Read the cycle time limit
cycleTime = int.Parse(input.ReadLine());
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
input.ReadLine();
// Read the processing times
for (int i = 0; i < nbTasks; ++i)
{
line = input.ReadLine().Split();
processingTime[i] = int.Parse(line[1]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
input.ReadLine();
// Read the successors' relations
while (true)
{
line = input.ReadLine().Split(',');
if (line[0] == "")
break;
int predecessor = int.Parse(line[0]) -1;
int successor = int.Parse(line[1]) -1;
if (successors[predecessor] == null)
successors[predecessor] = new List<int>();
successors[predecessor].Add(successor);
}
}
}
}
public class AssemblyLineBalancing : IDisposable
{
// LocalSolver
LocalSolver localsolver;
// Instance data
ALBInstance instance;
// Decision variables
LSExpression[] station;
// Intermediate expressions
LSExpression[] timeInStation;
LSExpression[] taskStation;
// Objective
LSExpression nbUsedStations;
// Constructor
public AssemblyLineBalancing(ALBInstance instance)
{
this.localsolver = new LocalSolver();
this.instance = instance;
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (localsolver != null)
localsolver.Dispose();
}
void Solve(int limit)
{
// Declare the optimization model
LSModel model = localsolver.GetModel();
// station[s] is the set of tasks assigned to station s
station = new LSExpression[instance.nbMaxStations];
LSExpression stationArray = model.Array();
for (int s = 0; s < instance.nbMaxStations; ++s)
{
station[s] = model.Set(instance.nbTasks);
stationArray.AddOperand(station[s]);
}
model.Constraint(model.Partition(stationArray));
// nbUsedStations is the total number of used stations
nbUsedStations = model.Sum();
for (int s = 0; s < instance.nbMaxStations; ++s)
nbUsedStations.AddOperand(model.Count(station[s]) > 0);
// All stations must respect the cycleTime constraint
timeInStation = new LSExpression[instance.nbMaxStations];
LSExpression processingTimeArray = model.Array(instance.processingTime);
LSExpression timeSelector = model.LambdaFunction(i => processingTimeArray[i]);
for (int s = 0; s < instance.nbMaxStations; ++s)
{
timeInStation[s] = model.Sum(station[s], timeSelector);
model.Constraint(timeInStation[s] <= instance.cycleTime);
}
// The stations must respect the succession's order of the tasks
taskStation = new LSExpression[instance.nbTasks];
for (int i = 0; i < instance.nbTasks; ++i)
{
taskStation[i] = model.Find(stationArray, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < instance.nbTasks; ++i)
if(instance.successors[i] != null)
foreach (int j in instance.successors[i])
model.Constraint(taskStation[i] <= taskStation[j]);
// Minimization of the number of active stations
model.Minimize(nbUsedStations);
model.Close();
// Parametrize the solver
localsolver.GetParam().SetTimeLimit(limit);
localsolver.Solve();
}
/* Write the solution in a file following the format:
* - 1st line: value of the objective
* - 2nd line: number of tasks
* - following lines: task's number, station's number */
void WriteSolution(string fileName)
{
using (StreamWriter output = new StreamWriter(fileName))
{
output.WriteLine(nbUsedStations.GetIntValue());
output.WriteLine(instance.nbTasks);
for (int i = 0; i < instance.nbTasks; ++i)
{
output.Write(i + 1);
output.Write(',');
output.WriteLine(taskStation[i].GetIntValue() + 1);
}
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (args.Length < 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Usage: AssemblyLineBalancing inputFile [solFile] [timeLimit]");
Environment.Exit(1);
}
string instanceFile = args[0];
string outputFile = args.Length > 1 ? args[1] : null;
string strTimeLimit = args.Length > 2 ? args[2] : "20";
ALBInstance instance = new ALBInstance(instanceFile);
using (AssemblyLineBalancing model = new AssemblyLineBalancing(instance))
{
model.Solve(int.Parse(strTimeLimit));
if (outputFile != null)
model.WriteSolution(outputFile);
}
}
}
- Compilation / Execution (Windows)
- javac AssemblyLineBalancing.java -cp %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolver.jarjava -cp %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolver.jar;. AssemblyLineBalancing instances\instance_n20_1.alb
- Compilation / Execution (Linux)
- javac AssemblyLineBalancing.java -cp /opt/localsolver_10_5/bin/localsolver.jarjava -cp /opt/localsolver_10_5/bin/localsolver.jar:. AssemblyLineBalancing instances/instance_n20_1.alb
/********** AssemblyLineBalancing.java **********/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import localsolver.*;
public class AssemblyLineBalancing {
private static class ALBInstance {
int nbTasks;
int nbMaxStations;
int cycleTime;
int[] processingTime;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> successors;
// Constructor
private ALBInstance(String fileName) throws IOException {
readInput(fileName);
}
// Read instance data
private void readInput(String fileName) throws IOException {
try (Scanner input = new Scanner(new File(fileName))) {
input.nextLine();
// Read number of tasks
nbTasks = input.nextInt();
nbMaxStations = nbTasks;
processingTime = new int[nbTasks];
successors = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(nbTasks);
for (int i = 0; i < nbTasks; i ++)
successors.add(i, new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
input.nextLine();
// Read the cycle time limit
cycleTime = input.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; ++i)
input.nextLine();
// Read the processing times
for (int i = 0; i < nbTasks; i++)
processingTime[input.nextInt()-1] = input.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
input.nextLine();
// Read the successors' relations
String line = input.nextLine();
while (!line.isEmpty()) {
String lineSplit[] = line.split(",");
int predecessor = Integer.parseInt(lineSplit[0]) -1;
int successor = Integer.parseInt(lineSplit[1]) -1;
successors.get(predecessor).add(successor);
line = input.nextLine();
}
}
}
}
private static class ALBProblem {
// LocalSolver
private final LocalSolver localsolver;
// Instance data
private final ALBInstance instance;
// Decision variables
private LSExpression[] station;
// Intermediate expressions
private LSExpression[] timeInStation;
private LSExpression[] taskStation;
// Objective
private LSExpression nbUsedStations;
// Constructor
private ALBProblem(LocalSolver localsolver, ALBInstance instance) {
this.localsolver = localsolver;
this.instance = instance;
}
private void solve(int limit) {
// Declare the optimization model
LSModel model = localsolver.getModel();
// station[s] is the set of tasks assigned to station s
station = new LSExpression[instance.nbMaxStations];
LSExpression stationArray = model.array();
for (int s = 0; s < instance.nbMaxStations; s++) {
station[s] = model.setVar(instance.nbTasks);
stationArray.addOperand(station[s]);
}
model.constraint(model.partition(stationArray));
// nbUsedStations is the total number of used stations
nbUsedStations = model.sum();
for (int s = 0; s < instance.nbMaxStations; s++) {
nbUsedStations.addOperand(model.gt(model.count(station[s]), 0));
}
// All stations must respect the cycleTime constraint
timeInStation = new LSExpression[instance.nbMaxStations];
LSExpression processingTimeArray = model.array(instance.processingTime);
LSExpression timeSelector = model.lambdaFunction(i -> model.at(processingTimeArray, i));
for (int s = 0; s < instance.nbMaxStations; s++) {
timeInStation[s] = model.sum(station[s], timeSelector);
model.constraint(model.leq(timeInStation[s], instance.cycleTime));
}
// The stations must respect the succession's order of the tasks
taskStation = new LSExpression[instance.nbTasks];
for (int i = 0; i < instance.nbTasks; i++) {
taskStation[i] = model.find(stationArray, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < instance.nbTasks; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> successors_i = instance.successors.get(i);
for (int j : successors_i) {
model.constraint(model.leq(taskStation[i], taskStation[j]));
}
}
// Minimization of the number of active stations
model.minimize(nbUsedStations);
model.close();
// Parametrize the solver
localsolver.getParam().setTimeLimit(limit);
localsolver.solve();
}
/* Write the solution in a file following the format:
* - 1st line: value of the objective
* - 2nd line: number of tasks
* - following lines: task's number, station's number */
void writeSolution(String fileName) throws IOException {
try(PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(fileName))) {
output.println(nbUsedStations.getIntValue());
output.println(instance.nbTasks);
for (int i = 0; i < instance.nbTasks; i++) {
output.print(i + 1);
output.print(",");
output.println(taskStation[i].getIntValue() + 1);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String [] args) {
if (args.length < 1) {
System.err.println("Usage: AssemblyLineBalancing inputFile [outputFile] [timeLimit]");
System.exit(1);
}
String instanceFile = args[0];
String outputFile = args.length > 1 ? args[1] : null;
String strTimeLimit = args.length > 2 ? args[2] : "20";
try (LocalSolver localsolver = new LocalSolver()) {
ALBInstance instance = new ALBInstance(instanceFile);
ALBProblem model = new ALBProblem(localsolver, instance);
model.solve(Integer.parseInt(strTimeLimit));
if (outputFile != null)
model.writeSolution(outputFile);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
