Curve Fitting¶
Principles learned¶
Add float decision variables
Minimize a non-linear objective
Create a non-linear expression with operators “sin” and “pow”
Problem¶
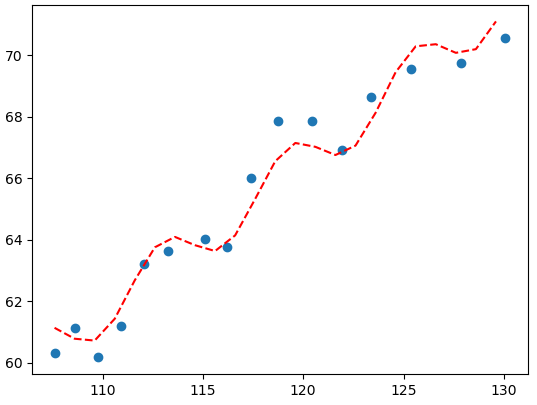
The curve fitting problem consists in finding the optimal parameters for a defined function to best map a set of inputs to a set of outputs.
For example, here we assume the mapping function has the form:
We want to find the parameters a, b, c, d
for which the mapping function best fits the observations.
Data¶
Each data file contains:
First line: the number of observations
Next lines : values of input and output for each observation
Program¶
The decision variables are the parameters of the mapping function: a, b, c, d.
The objective is to minimize the sum of square errors. For a given input,
the square error is the squared difference between the
output predicted by the mapping function and the observed output.
- Execution:
- localsolver curve_fitting.lsp instances/observations.in [lsTimeLimit=] [solFileName=]
/********** curve_fitting.lsp **********/
use io;
/* Reads instance data. */
function input() {
local usage = "Usage: localsolver curve_fitting.lsp "
+ "inFileName=inputFile [solFileName=outputFile] [lsTimeLimit=timeLimit]";
if (inFileName == nil) throw usage;
local inFile = io.openRead(inFileName);
nbObervations = inFile.readInt();
for [i in 1..nbObervations]{
inputs[i] = inFile.readDouble();
outputs[i] = inFile.readDouble();
}
}
/* Declares the optimization model. */
function model() {
// parameters of the mapping function
a <- float(-100, 100);
b <- float(-100, 100);
c <- float(-100, 100);
d <- float(-100, 100);
// minimize square error between prediction and output
predictions[i in 1..nbObervations] <- a * sin(b - inputs[i]) + c * pow(inputs[i], 2) + d;
errors[i in 1..nbObervations] <- predictions[i] - outputs[i];
squareError <- sum[i in 1..nbObervations] (pow(errors[i], 2));
minimize squareError;
}
/* Parameterizes the solver. */
function param() {
if (lsTimeLimit == nil) lsTimeLimit = 3;
}
/* Writes the solution in a file */
function output() {
if (solFileName == nil) return;
local solFile = io.openWrite(solFileName);
solFile.println("Optimal mapping function");
solFile.println("a = " + a.value);
solFile.println("b = " + b.value);
solFile.println("c = " + c.value);
solFile.println("d = " + d.value);
}
- Execution (Windows)
- set PYTHONPATH=%LS_HOME%\bin\pythonpython curve_fitting.py instances\observations.in
- Execution (Linux)
- export PYTHONPATH=/opt/localsolver_11_0/bin/pythonpython curve_fitting.py instances/observations.in
########## curve_fitting.py ##########
import localsolver
import sys
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python curve_fitting.py inputFile [outputFile] [timeLimit]")
sys.exit(1)
def read_float(filename):
with open(filename) as f:
return [float(elem) for elem in f.read().split()]
with localsolver.LocalSolver() as ls:
#
# Reads instance data
#
file_it = iter(read_float(sys.argv[1]))
# Number of observations
nb_observations = int(next(file_it))
# Inputs and outputs
inputs = []
outputs = []
for i in range(nb_observations):
inputs.append(next(file_it))
outputs.append(next(file_it))
#
# Declares the optimization model
#
model = ls.model
# Decision variables : parameters of the mapping function
a = model.float(-100, 100)
b = model.float(-100, 100)
c = model.float(-100, 100)
d = model.float(-100, 100)
# Minimize square error between prediction and output
predictions = [a * model.sin(b - inputs[i]) + c * inputs[i] ** 2 + d for i in range(nb_observations)]
errors = [predictions[i] - outputs[i] for i in range(nb_observations)]
square_error = model.sum(model.pow(errors[i], 2) for i in range(nb_observations))
model.minimize(square_error)
model.close()
#
# Parameterizes the solver
#
if len(sys.argv) >= 4:
ls.param.time_limit = int(sys.argv[3])
else:
ls.param.time_limit = 3
ls.solve()
#
# Writes the solution in a file
#
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
with open(sys.argv[2], 'w') as f:
f.write("Optimal mapping function\n")
f.write("a = " + str(a.value) + "\n")
f.write("b = " + str(b.value) + "\n")
f.write("c = " + str(c.value) + "\n")
f.write("d = " + str(d.value) + "\n")
- Compilation / Execution (Windows)
- cl /EHsc curve_fitting.cpp -I%LS_HOME%\include /link %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolver110.libcurve_fitting instances\observations.in
- Compilation / Execution (Linux)
- g++ curve_fitting.cpp -I/opt/localsolver_11_0/include -llocalsolver110 -lpthread -o curve_fitting./curve_fitting instances/observations.in
//********* curve_fitting.cpp *********
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include "localsolver.h"
using namespace localsolver;
using namespace std;
class CurveFitting {
public:
// Number of observations
int nbObservations;
// Inputs and Outputs
vector<lsdouble> inputs;
vector<lsdouble> outputs;
// Solver
LocalSolver localsolver;
// Decision variables (parameters of the mapping function)
LSExpression a, b, c, d;
// Objective (square error)
LSExpression squareError;
// Reads instance data
void readInstance(const string& fileName) {
ifstream infile;
infile.exceptions(ifstream::failbit | ifstream::badbit);
infile.open(fileName.c_str());
infile >> nbObservations;
inputs.resize(nbObservations);
outputs.resize(nbObservations);
for (int i = 0; i < nbObservations; i++) {
infile >> inputs[i];
infile >> outputs[i];
}
}
void solve(int limit) {
// Declares the optimization model
LSModel model = localsolver.getModel();
// Decision variables
a = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
b = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
c = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
d = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
// Minimize square error
squareError = model.sum();
for (int i = 0; i < nbObservations; i++) {
LSExpression prediction = a * model.sin(b - inputs[i]) + c * pow(inputs[i], 2) + d;
LSExpression error = model.pow(prediction - outputs[i], 2);
squareError.addOperand(error);
}
model.minimize(squareError);
model.close();
// Parameterizes the solver.
localsolver.getParam().setTimeLimit(limit);
localsolver.solve();
}
// Writes the solution in a file
void writeSolution(const string& fileName) {
ofstream outfile;
outfile.exceptions(ofstream::failbit | ofstream::badbit);
outfile.open(fileName.c_str());
outfile << "Optimal mapping function" << endl;
outfile << "a = " << a.getDoubleValue() << endl;
outfile << "b = " << b.getDoubleValue() << endl;
outfile << "c = " << c.getDoubleValue() << endl;
outfile << "d = " << d.getDoubleValue() << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc < 2) {
cerr << "Usage: curve_fitting inputFile [outputFile] [timeLimit]" << endl;
return 1;
}
const char* instanceFile = argv[1];
const char* solFile = argc > 2 ? argv[2] : NULL;
const char* strTimeLimit = argc > 3 ? argv[3] : "3";
try {
CurveFitting model;
model.readInstance(instanceFile);
model.solve(atoi(strTimeLimit));
if (solFile != NULL) model.writeSolution(solFile);
return 0;
} catch (const exception& e) {
cerr << "An error occurred: " << e.what() << endl;
return 1;
}
}
- Compilation / Execution (Windows)
- copy %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolvernet.dll .csc CurveFitting.cs /reference:localsolvernet.dllCurveFitting instances\observations.in
/********** CurveFitting.cs **********/
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Globalization;
using localsolver;
public class CurveFitting : IDisposable
{
// Number of observations
int nbObservations;
// Inputs and Outputs
double[] inputs;
double[] outputs;
// Solver
LocalSolver localsolver;
// Decision variables (parameters of the mapping function)
LSExpression a, b, c, d;
// Objective (square error)
LSExpression squareError;
public CurveFitting()
{
localsolver = new LocalSolver();
}
// Reads instance data
void ReadInstance(string fileName)
{
using (StreamReader input = new StreamReader(fileName))
{
nbObservations = int.Parse(input.ReadLine());
inputs = new double[nbObservations];
outputs = new double[nbObservations];
for (int i = 0; i < nbObservations; i++)
{
string[] splittedObs = input.ReadLine().Split(' ');
inputs[i] = double.Parse(splittedObs[0], CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
outputs[i] = double.Parse(splittedObs[1], CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
}
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (localsolver != null)
localsolver.Dispose();
}
void Solve(int limit)
{
// Declares the optimization model
LSModel model = localsolver.GetModel();
// Decision variables
a = model.Float(-100, 100);
b = model.Float(-100, 100);
c = model.Float(-100, 100);
d = model.Float(-100, 100);
// Minimize square error
squareError = model.Sum();
for (int i = 0; i < nbObservations; i++)
{
LSExpression prediction = a * model.Sin(b - inputs[i]) + c * Math.Pow(inputs[i], 2) + d;
LSExpression error = model.Pow(prediction - outputs[i], 2);
squareError.AddOperand(error);
}
model.Minimize(squareError);
model.Close();
// Parameterizes the solver
localsolver.GetParam().SetTimeLimit(limit);
localsolver.Solve();
}
// Writes the solution in a file
void WriteSolution(string fileName)
{
using (StreamWriter output = new StreamWriter(fileName))
{
output.WriteLine("Optimal mapping function");
output.WriteLine("a = " + a.GetDoubleValue());
output.WriteLine("b = " + b.GetDoubleValue());
output.WriteLine("c = " + c.GetDoubleValue());
output.WriteLine("d = " + d.GetDoubleValue());
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (args.Length < 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Usage: CurveFitting inputFile [solFile] [timeLimit]");
Environment.Exit(1);
}
string instanceFile = args[0];
string outputFile = args.Length > 1 ? args[1] : null;
string strTimeLimit = args.Length > 2 ? args[2] : "3";
using (CurveFitting model = new CurveFitting())
{
model.ReadInstance(instanceFile);
model.Solve(int.Parse(strTimeLimit));
if (outputFile != null)
model.WriteSolution(outputFile);
}
}
}
- Compilation / Execution (Windows)
- javac CurveFitting.java -cp %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolver.jarjava -cp %LS_HOME%\bin\localsolver.jar;. CurveFitting instances\observations.in
- Compilation / Execution (Linux)
- javac CurveFitting.java -cp /opt/localsolver_11_0/bin/localsolver.jarjava -cp /opt/localsolver_11_0/bin/localsolver.jar:. CurveFitting instances/observations.in
/********** CurveFitting.java **********/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import localsolver.*;
public class CurveFitting {
// Number of observations
private int nbObservations;
// Inputs and Outputs
private double[] inputs;
private double[] outputs;
// Solver
private final LocalSolver localsolver;
// Decision variables (parameters of the mapping function)
private LSExpression a, b, c, d;
// Objective (square error)
private LSExpression squareError;
private CurveFitting(LocalSolver localsolver) {
this.localsolver = localsolver;
}
// Reads instance data
private void readInstance(String fileName) throws IOException {
try (Scanner input = new Scanner(new File(fileName))) {
input.useLocale(Locale.ROOT);
nbObservations = input.nextInt();
inputs = new double[nbObservations];
outputs = new double[nbObservations];
for (int i = 0; i < nbObservations; i++) {
inputs[i] = input.nextDouble();
outputs[i] = input.nextDouble();
}
}
}
private void solve(int limit) {
// Declares the optimization model
LSModel model = localsolver.getModel();
// Decision variables
a = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
b = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
c = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
d = model.floatVar(-100, 100);
// Minimize square error
squareError = model.sum();
for (int i = 0; i < nbObservations; i++) {
LSExpression prediction = model.sum(model.prod(a, model.sin(model.sub(b, inputs[i]))), model.prod(c, Math.pow(inputs[i], 2)), d);
LSExpression error = model.pow(model.sub(prediction, outputs[i]), 2);
squareError.addOperand(error);
}
model.minimize(squareError);
model.close();
// Parameterizes the solver
localsolver.getParam().setTimeLimit(limit);
localsolver.solve();
}
// Writes the solution in a file
private void writeSolution(String fileName) throws IOException {
try (PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter(fileName)) {
output.println("Optimal mapping function");
output.println("a = " + a.getDoubleValue());
output.println("b = " + b.getDoubleValue());
output.println("c = " + c.getDoubleValue());
output.println("d = " + d.getDoubleValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length < 1) {
System.err.println("Usage: java CurveFitting inputFile [outputFile] [timeLimit]");
System.exit(1);
}
String instanceFile = args[0];
String outputFile = args.length > 1 ? args[1] : null;
String strTimeLimit = args.length > 2 ? args[2] : "3";
try (LocalSolver localsolver = new LocalSolver()) {
CurveFitting model = new CurveFitting(localsolver);
model.readInstance(instanceFile);
model.solve(Integer.parseInt(strTimeLimit));
if (outputFile != null) {
model.writeSolution(outputFile);
}
} catch(Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
